A diabetes diagnosis can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re suddenly faced with unfamiliar terms like insulin, blood sugar, and home testing. But the truth is, feline diabetes is manageable—and with knowledge and the right tools, many cats go on to live healthy, happy lives.
Understanding what diabetes actually is—and what it isn’t—is the best place to start.
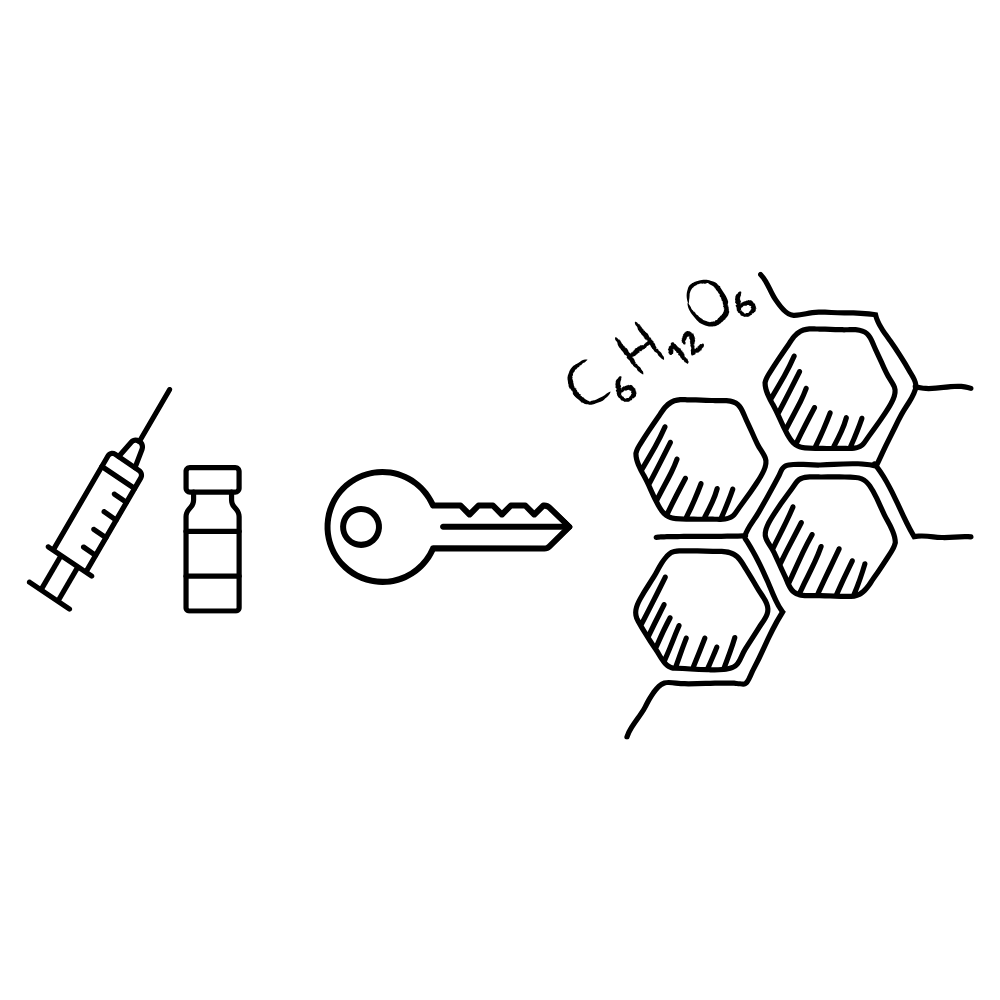
The Role of Sugar and Insulin
Every cell in a cat’s body needs sugar (glucose) to function. Glucose provides energy for everything from nerve signals to muscle movement to cell regeneration. But glucose can’t enter cells on its own—it needs help. That help comes from insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas.
Think of insulin as a key that unlocks the cell’s door. Without insulin, sugar remains trapped in the bloodstream, unable to fuel the cells that need it. When this happens, the body tries to compensate: the liver stores what it can, the kidneys attempt to flush out the excess, and the result is elevated blood sugar, increased urination, extreme thirst, and often weight loss.
In diabetic cats, the pancreas either doesn’t produce enough insulin or the insulin it produces isn’t effective. This disrupts the body’s ability to use glucose properly, and over time, it can lead to serious health complications.
What Causes Diabetes in Cats?
Feline diabetes can have many causes—sometimes temporary, sometimes permanent. Contributing factors may include obesity, high-carbohydrate diets, chronic inflammation, pancreatitis, certain medications like steroids, or even genetic predisposition. In some cases, the insulin-producing cells (beta cells) of the pancreas become exhausted or damaged. Without enough insulin, the body can’t move glucose into the cells, and energy production breaks down.
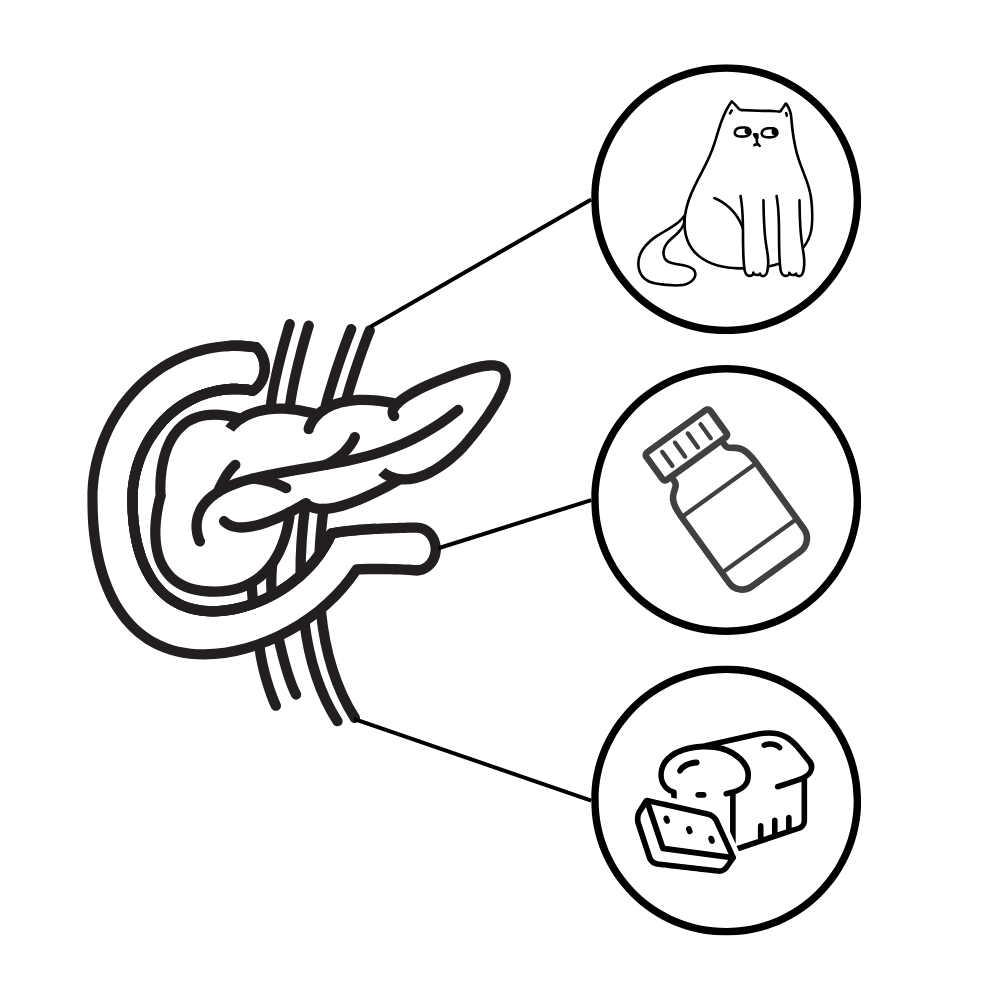
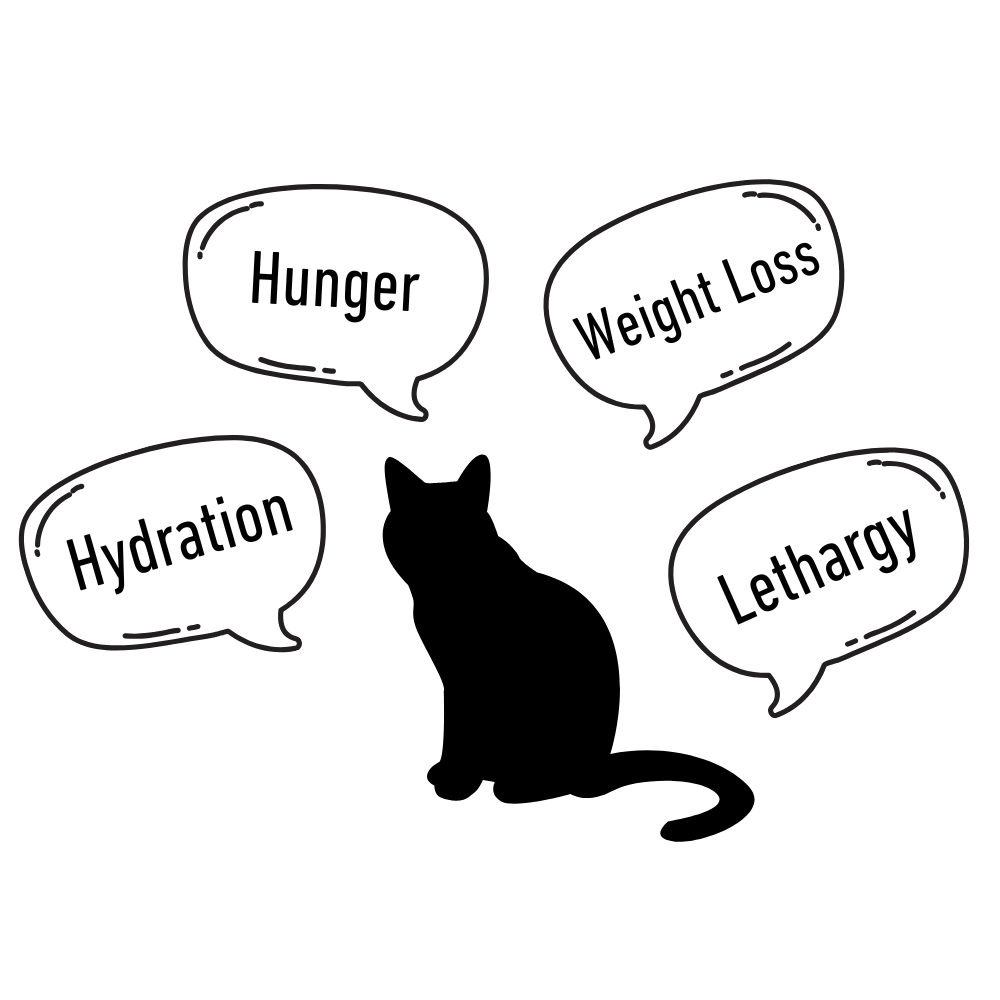
Why Are the Symptoms So Severe?
When glucose can’t enter the cells, the body starts to behave as if it’s starving—even though there’s plenty of sugar in the blood. That triggers hunger, even as weight drops. The kidneys try to flush out the excess sugar, leading to frequent urination and dehydration. Without energy, the body begins breaking down fat and muscle to survive, which can lead to ketone production—a dangerous condition that may result in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
How Insulin Treatment Works
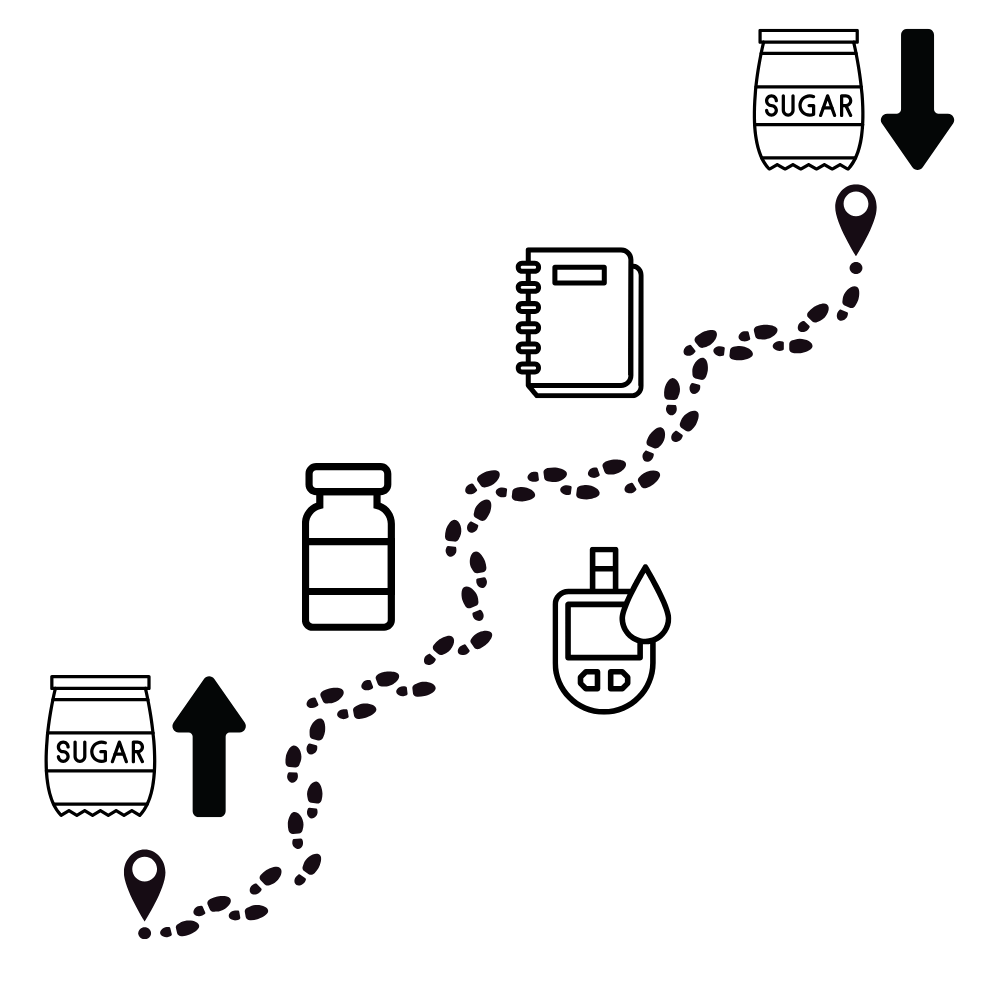
When we give insulin by injection, we’re replacing the hormone the body can no longer produce in adequate amounts. The goal is to help glucose move from the blood into the cells so the body can function normally again. Over time, symptoms improve: appetite stabilizes, thirst and urination normalize, weight returns, and energy levels rise. This only happens when insulin is given in the right amount—enough to do the job, but not so much that it causes dangerously low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
This is why home blood glucose monitoring is so important. By tracking how your cat responds to insulin, you can make informed decisions and avoid overcorrection. Finding the right insulin dose is a process of observation, patience, and adjustment.
Diet Matters
Unlike humans, cats are obligate carnivores. Their bodies are designed to derive energy from protein, not carbohydrates. High-carb diets can spike blood glucose and worsen insulin resistance. That’s why many diabetic cats do best on a low-carb, high-protein diet. In fact, for some cats, changing the diet alone—especially early in the disease—can dramatically reduce or even eliminate the need for insulin.
However, it’s crucial to monitor blood sugar closely if you change your cat’s food. Reducing carbs while giving the same dose of insulin can cause hypoglycemia. Always adjust one variable at a time, and test frequently to stay ahead of changes.

The Danger of Low Blood Sugar
While high blood sugar is a long-term concern, low blood sugar can become life-threatening in minutes. Too much insulin, especially in combination with dietary changes or missed meals, can push blood sugar dangerously low. Signs of hypoglycemia can range from hunger and lethargy to seizures and coma. Prompt treatment with fast-acting sugar (like corn syrup or honey) can be life-saving.
This is why you’ll often hear the phrase: “Start low, go slow.” Start with a conservative insulin dose, increase gradually, and test often to prevent overdosing. Over time, you’ll learn how your cat’s body responds and how to maintain a safe balance.
The Big Picture
Feline diabetes is manageable, especially once you understand the basic biology: glucose needs insulin to get into cells, and insulin needs to be balanced with food and the body’s needs. When things fall out of balance, the system starts to break down. But with insulin, the right diet, and a little patience, your cat can return to a healthy, stable life.
In some cases, diabetic cats can even go into remission, meaning they no longer need insulin. This happens when the pancreas recovers enough function to manage blood sugar on its own—a possibility that makes feline diabetes unique.

What's Next?
Check out some of our blog articles that go into each of these topics more in-depth.









